How does a wifi extender work: A simple guide
- Craig Marston
- Oct 25, 2025
- 14 min read
Updated: Nov 5, 2025
At its simplest, a WiFi extender grabs the wireless signal from your router and gives it a boost, rebroadcasting it into areas of your home or office where the connection is weak or non-existent.
Think of it as a relay team for your internet. The extender picks up the signal just as it starts to fade and then passes it on with renewed strength. This simple two-step process—receive and transmit—is the secret to getting rid of those frustrating WiFi 'dead zones' for good.
How WiFi Extenders Boost Your Signal

At its heart, a WiFi extender is a straightforward fix for a very common problem. Your main router has a finite range, and things like thick brick walls, floors, or even large furniture can seriously get in the way of its signal. An extender acts as a bridge, filling in the gaps where your primary network just can't reach reliably.
Let's use an analogy. Imagine your router is trying to shout a message across a large, noisy room. The further you are from the router, the fainter that message gets, until eventually, you can't hear it at all. A WiFi extender is like having a friend standing halfway across the room. They listen carefully to the original message and then shout it out again, making sure it reaches every corner with perfect clarity. That's exactly how it works with your internet signal.
The Two-Step Process Explained
The way an extender operates is beautifully simple, boiling down to two key actions:
Receiving the Signal: First, the extender uses its internal antennas to lock onto your existing WiFi network. For this to work well, you need to plug the extender in somewhere it can still get a decent, stable connection from your main router.
Transmitting a New Signal: Once it has a solid connection, the extender broadcasts a brand new wireless signal. Your phone, laptop, or smart TV in the previously dead zone connects to this new signal, giving you internet access where you had nothing before.
This process essentially creates a bigger bubble of wireless coverage around your property. It’s a tried-and-tested method for improving your network without needing to rip everything out and start again.
To break it down even further, here's a quick summary of how the components work together.
How a WiFi Extender Functions
Component or Action | What It Does for Your Network | The End Result for You |
|---|---|---|
Placement | Placed between your router and the dead zone | Fills in the coverage gaps |
Receiving Antennas | Capture the existing WiFi signal from your router | The extender gets a stable connection |
Rebroadcasting | Transmits a new, boosted signal | Your devices can connect in weak areas |
New Network (SSID) | Creates a separate network (e.g., "HomeWiFiEXT") | A clear, strong signal for you to join |
This all comes together to give you a seamless online experience, even in the furthest corners of your property.
Why Signal Strength Matters
Your network name, or SSID (Service Set Identifier), is what you see when you look for WiFi networks on your device. An extender usually creates a new network with a similar name, often just adding "_EXT" to your original one. When you move into a dead zone, you simply switch your device over to this extended network.
This technology is particularly useful here in the United Kingdom. With over 95% of UK households having WiFi, the common building materials like brick and stone are a nightmare for signal strength. WiFi extenders overcome this by grabbing the wireless signal and pushing it out again, amplifying it by up to 300% in those dead zones to ensure you stay connected.
This is absolutely vital for remote work, streaming your favourite shows, and online learning. If you're interested in the numbers, you can explore more about this trend and the growing WiFi extender market.
Understanding the Technology Inside
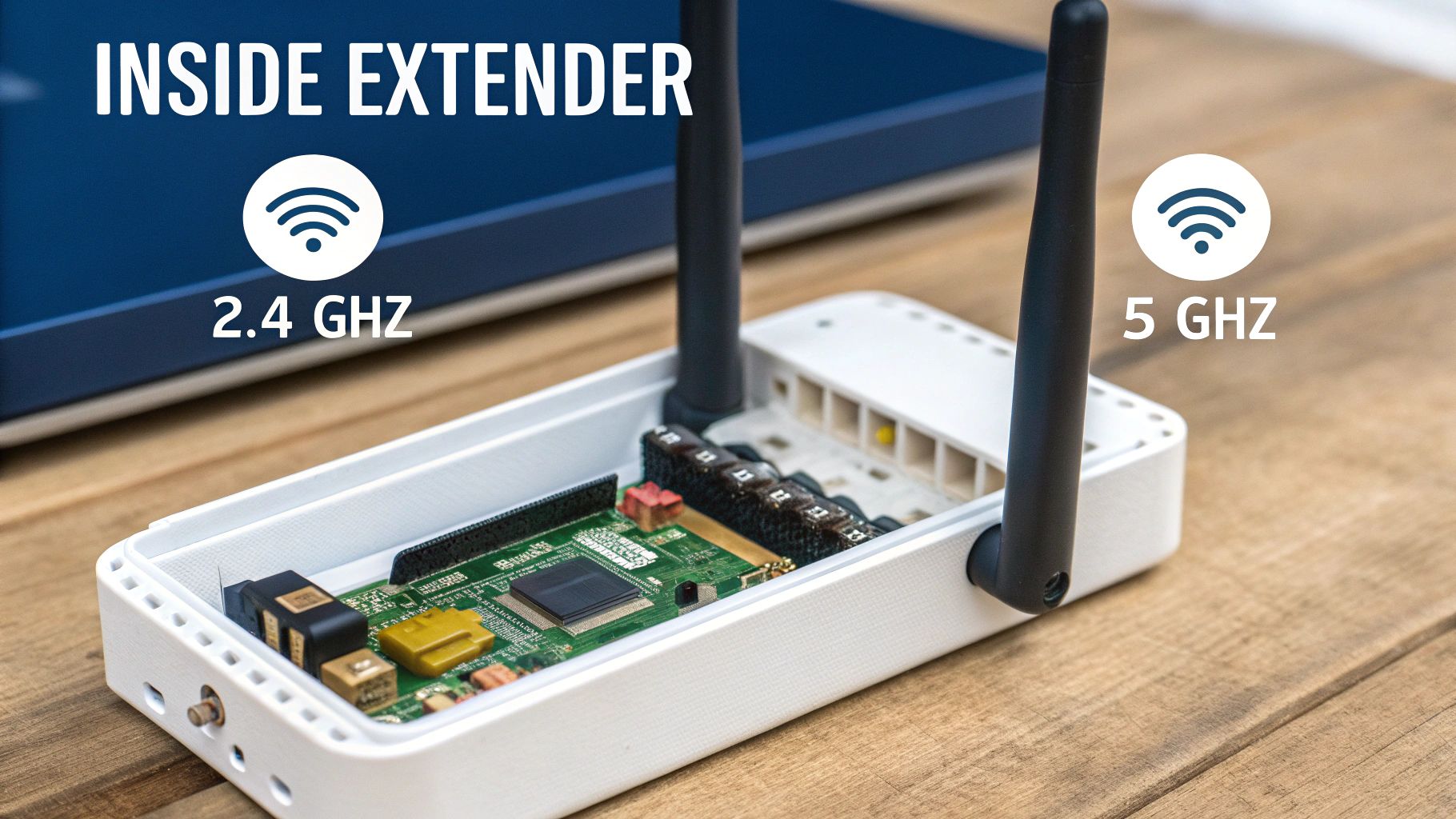
So we've covered what a Wi-Fi extender does. Now, let’s peel back the cover and look at how the technology inside gets the job done. The real performance of these handy devices comes down to their internal antennas, processors, and the wireless frequencies they use to talk to your router and your gadgets.
At the heart of it all are two main frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. You can think of them as different lanes on a motorway for your data traffic.
The Two Lanes of Wi-Fi Traffic
Getting your head around the difference between these two bands is the key to understanding how an extender works and how to get the most out of it. Each one has its own strengths, making it better suited for certain situations.
2.4 GHz – The All-Terrain Vehicle: This band is brilliant at covering long distances and pushing through solid obstacles like thick walls and floors. The trade-off? It’s slower and much more likely to get congested by interference from other common household devices, like microwaves and cordless phones.
5 GHz – The Sports Car: This frequency delivers much faster speeds and a clearer, less crowded connection. It’s perfect for bandwidth-hungry tasks like streaming high-definition video or online gaming. Its main weakness is a shorter range and a poorer ability to penetrate solid objects.
Any quality extender will use both bands to give you a flexible and reliable connection. This dual-band capability is essential for creating a certified, tested network delivery that can handle everything you throw at it, from checking emails in the garden to streaming a film in the loft.
Why Your Connection Can Sometimes Slow Down
Here’s a crucial concept to grasp about how many Wi-Fi extenders operate: half-duplex communication. In simple terms, a lot of basic extenders can't receive and transmit data at the same time on the same frequency band. It’s a bit like using a walkie-talkie—only one person can talk at once.
This one-way traffic flow effectively cuts the available bandwidth in half for any device connected to the extender. This isn't a fault; it’s just a fundamental limitation of the technology that can cause a noticeable drop in speed.
Thankfully, modern extenders have a clever way around this called cross-band technology. These devices can receive the signal from your router on one band (say, 5 GHz) and then broadcast it to your devices on the other (2.4 GHz), completely avoiding that half-duplex bottleneck. This clever trick ensures a much more stable and speedy connection, often backed by a robust 25-year equipment warranty for long-term peace of mind.
While extenders are great at amplifying a signal, they do introduce a tiny delay, or latency. Performance data shows a typical Wi-Fi extender in the UK might add a 5 to 15-millisecond delay, which can be critical for latency-sensitive tasks like video calls.
As UK homes now average over eight connected devices, newer extenders supporting Wi-Fi 6 are becoming vital. They can offer speeds up to 9.6 Gbps in ideal conditions, providing the capacity needed for today's connected households. For a deeper dive into the technicals, you can explore the findings on the home Wi-Fi extender market.
Finding the Perfect Spot for Your Extender
Knowing how the technology works is one thing, but knowing where to actually put your extender is the real secret to unlocking its potential. The location is absolutely critical for performance, and getting it right can turn a frustratingly patchy connection into a solid, reliable one.
Think of it as finding the perfect halfway point in a conversation. If you're too close to the person speaking, you're just repeating what everyone can already hear. But if you're too far away, you'll only catch a garbled mess, and that's what you'll end up repeating.
The ideal placement for your extender is about halfway between your main router and the Wi-Fi dead zone you want to fix. If it’s too close to the router, its rebroadcasted signal simply won’t have the reach you need. On the flip side, if you place it too far away, it will only pick up an already weak and unstable signal, which just leads to poor performance and constant dropouts.
Locating the Sweet Spot
Finding this perfect middle ground doesn't require any complicated tools; you can get a surprisingly good idea of signal quality just by using your smartphone.
Start at your router and walk towards the dead zone, keeping a close eye on the Wi-Fi icon on your phone. The best spot for the extender is where you still have at least two or three bars of signal strength. This ensures the extender receives a strong, stable connection that it can then rebroadcast effectively.
For a more precise, data-driven approach, you might want to look into how to professionally test Wi-Fi signal strength in your UK home. This gives you the hard numbers needed for a truly certified network delivery.
The goal is simple: place the extender where the signal from your router is still strong enough to be effectively amplified. A weak input signal will always result in a weak output, no matter how powerful the extender is.
Avoiding Common Signal Blockers
Once you’ve found a general area, you also need to consider what’s around it. Certain everyday items in your home or office are notorious for causing Wi-Fi interference, and placing your extender near them can seriously sabotage its performance.
Be sure to keep your extender away from these common culprits:
Microwave Ovens: These operate on the 2.4 GHz frequency and can cause significant interference whenever they're running.
Thick Concrete or Brick Walls: Just like with your main router, these dense materials are very effective at blocking Wi-Fi signals.
Large Metal Objects: Things like metal filing cabinets, refrigerators, or even large mirrors can reflect and disrupt wireless signals.
Cordless Phones and Baby Monitors: Many of these devices also use the 2.4 GHz band, creating signal "noise" that can slow your connection down.
By carefully choosing a location that balances distance while avoiding interference, you give your extender the best possible chance to do its job properly. This strategic placement is fundamental to making it work effectively and delivering the reliable connectivity you need.
Extenders vs Mesh vs Powerline Adapters
Knowing how a WiFi extender works is one thing, but knowing when it’s the right tool for the job is another entirely. While an extender is a fantastic, budget-friendly way to patch up a specific dead zone, it’s not your only option. To make the right call, you need to weigh it against two other popular bits of kit: mesh WiFi systems and powerline adapters.
Each of these is built to solve a different kind of connectivity headache. The best choice for you will come down to your property’s layout, what kind of performance you need, and of course, your budget. Let's break them down so you can figure out which one will give you a reliable network exactly where you need it.
This simple diagram shows the thought process for placing an extender, focusing on getting the balance right between signal strength and physical barriers.
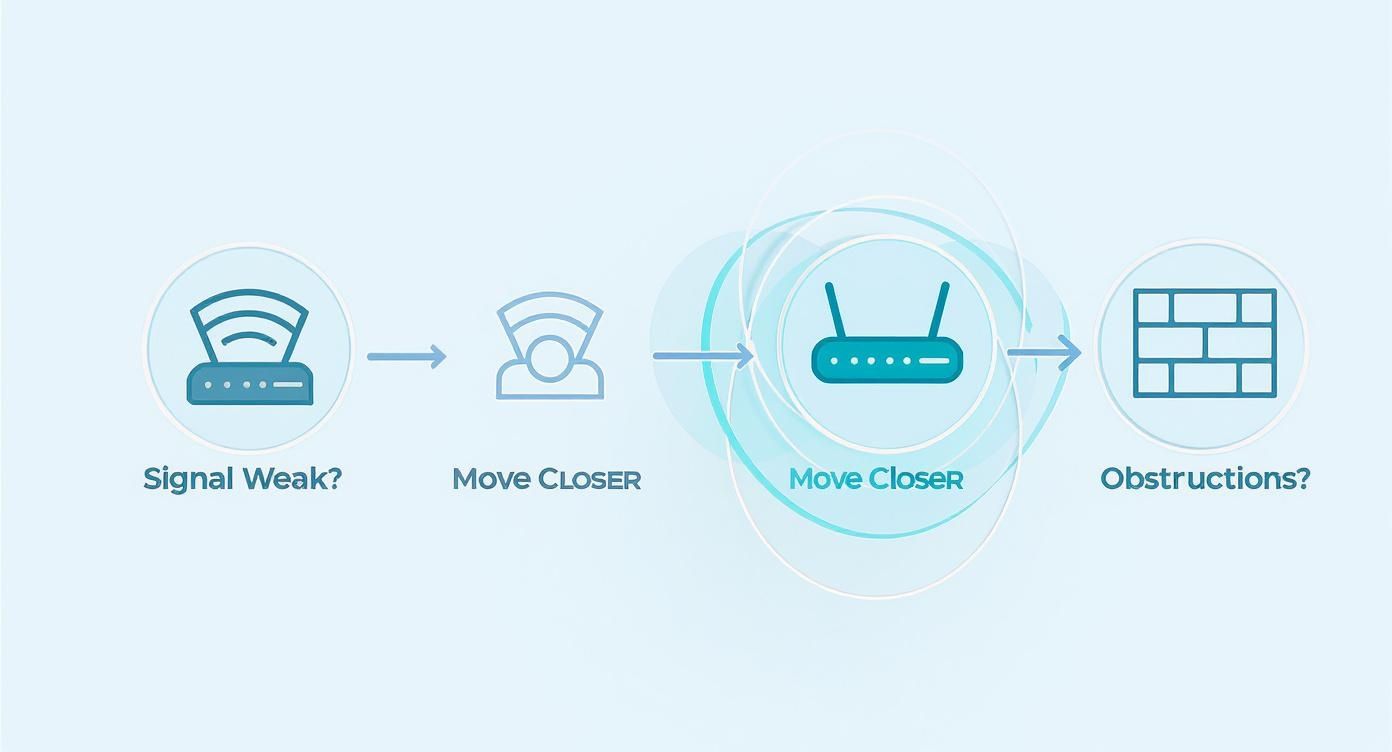
The trick is finding that sweet spot: close enough to the router to get a strong signal, but far enough away to push that signal into the room that needs it.
WiFi Extenders: The Focused Fix
Think of a WiFi extender as your go-to for small, well-defined problem areas. If you’ve got one or two rooms—maybe a loft office or a back conservatory—where the signal just gives up, an extender is almost always the most cost-effective and straightforward fix.
Best For: Small to medium-sized homes or offices with specific, isolated dead zones.
How It Works: It grabs your existing wireless signal and simply rebroadcasts it, creating a new, extended network to connect to.
Consideration: As we've covered, this often means a separate network name (SSID) and can cut your available bandwidth in half due to its one-at-a-time communication method.
Mesh WiFi Systems: Whole-Property Coverage
For larger properties or situations where seamless coverage is a must, a mesh system is a much more powerful solution. Instead of a single box repeating a signal, a mesh system uses multiple ‘nodes’ dotted around your property to create one big, intelligent network.
A mesh system completely replaces your existing router's WiFi, blanketing your entire space with a single, strong signal under one network name. Your devices automatically hop to the strongest node as you move around, so you never have to manually switch networks.
This is the ideal approach for large offices or multi-storey homes where consistent, reliable connectivity is non-negotiable. It’s a bigger investment, but the user experience is far superior, especially for a business. You can dive deeper into why this is a game-changer in our guide to mesh network advantages your UK office needs. As an Excel network accredited partner, we ensure these systems are installed to the highest certified standards.
Powerline Adapters: The Specialist Tool
Finally, we have powerline adapters—the specialist problem-solvers. This clever technology uses your building’s own electrical wiring to carry the internet signal. One adapter plugs into a socket near your router and connects via an Ethernet cable; the other plugs in near the dead zone, instantly turning that socket into a network access point.
Best For: Getting around thick stone walls, concrete floors, or other major physical obstacles that wireless signals just can’t get through.
How It Works: It sends data through your copper electrical circuits, completely bypassing any wireless interference.
Consideration: The performance you get heavily depends on the quality and age of your building's wiring.
Which Network Booster is Right for You?
Choosing between these three options can feel tricky, but it really boils down to what specific problem you're trying to solve. An extender is a quick fix for a small area, a mesh system is a whole-home upgrade, and a powerline adapter is for when walls get in the way.
Here’s a direct comparison to help you decide.
Feature | WiFi Extender | Mesh WiFi System | Powerline Adapter |
|---|---|---|---|
Best Use Case | Small, specific dead zones (1-2 rooms) | Whole-home or office coverage | Rooms with thick walls or floors |
Performance | Decent, but can halve bandwidth | Excellent, consistent speeds everywhere | Very reliable, but depends on electrical wiring quality |
Network Name (SSID) | Usually creates a separate network | One single, unified network | Can create a separate or unified network (varies by model) |
Ease of Setup | Very easy; plug-and-play | Moderate; replaces your existing router | Easy; plug into sockets and pair |
Cost | £ (Most affordable) | £££ (Highest initial investment) | ££ (Mid-range) |
Scalability | Limited; adding more can create issues | Highly scalable; add more nodes to expand | Limited; performance degrades with too many adapters |
Ultimately, the best solution is the one that fits your space and your needs. If you’re just trying to get a better signal in the kitchen, an extender is probably all you need. But if you’re tired of dropped connections all over the house, it might be time to look at a mesh system.
When a WiFi Extender Is the Perfect Solution
Knowing the theory behind WiFi extenders is one thing, but seeing where they genuinely solve real-world problems is what really matters. Extenders shine in very specific situations, offering a targeted, budget-friendly boost right where you need it most. Think of them as the perfect tool for patching up those frustrating dead zones without having to rip out and replace your entire network setup.
Let’s walk through a few common scenarios where an extender is the ideal fix. By looking at these practical applications, you’ll probably recognise some of the network challenges you’re facing at home and see how a simple plug-in device can bring back reliable, consistent connectivity.
Solving Common Household Dead Zones
Most UK homes have those predictable spots where the WiFi just gives up. It could be the spare room at the far end of the house or the newly converted loft. These are prime candidates for an extender, which can deliver a certified, tested network delivery exactly where it’s needed.
Here are a few classic examples:
The Loft Conversion Home Office: You’ve finally set up the perfect workspace, but the WiFi signal is so weak it can barely handle an email, let alone a video call. Placing an extender on the first-floor landing acts as a relay. It grabs the strong signal from your downstairs router and pushes it upwards, giving you a stable connection to get your work done.
The Conservatory Smart TV: Trying to stream your favourite series in the conservatory is an exercise in frustration, with constant buffering ruining the experience. An extender plugged into a nearby dining room socket can punch a reliable signal through to the TV, ensuring your streaming is smooth and uninterrupted.
The Garden Patio: On a rare sunny evening, you want to sit outside and stream some music or browse the web. By placing an extender in a room closest to the garden, you can push your WiFi coverage outdoors and turn your patio into a fully connected space.
By targeting these specific problem areas, a WiFi extender offers a precise and affordable solution. It solves the immediate issue of a dead zone without the expense or complexity of a full network replacement, often supported by a 25 year equipment warranty for added peace of mind.
It’s no surprise the demand for these devices is growing. The WiFi extender market in Europe now accounts for over 30% of the global share, with a value topping USD 400 million. With nearly 40% of the UK workforce now in remote or hybrid roles, the need for dependable home coverage has shot up, making extenders a go-to choice for doubling a network’s range. For those interested, you can find more detail on the WiFi range extender market on cognitivemarketresearch.com.
These examples show how an extender helps you get the most out of your existing connection. If you're curious about what a good signal range actually looks like, you can learn more by reading our guide on how far WiFi should reach.
Common WiFi Extender Myths Debunked
To make a smart decision about your network, you first need to separate the facts from the marketing fluff. A lot of the frustration people have with WiFi extenders comes from simple misunderstandings about what they can and can’t do. Let's clear the air and bust some of the biggest myths.
This will help you set realistic expectations and find the right solution, whether that’s a simple extender or a more robust network upgrade involving professional fibre cable installation.
Myth 1: An Extender Will Make My Internet Faster
This is probably the most common misconception out there. A WiFi extender is designed to stretch the range of your wireless signal, not boost the speed of your internet plan. It simply catches your existing signal and rebroadcasts it.
Think of it this way: if the signal it receives is slow and weak, the signal it sends out will also be slow and weak. Its job is to get a usable connection into a dead zone, not to magically make your broadband faster.
Myth 2: You Can Just Plug It in Anywhere
As we’ve already touched on, placement is everything. Jamming an extender right in the middle of a dead zone is a guaranteed recipe for disappointment because it has no decent signal to work with in the first place.
You need to find that sweet spot, which is almost always halfway between your router and the area with poor signal. It needs to be close enough to the router to pick up a strong, stable signal to pass on.
The rule is simple: a weak signal going in means a weak signal coming out. Getting the location right is essential for a certified, tested network delivery that provides a stable connection where you need it most.
Picking the right gear and placing it correctly is the difference between a frustrating network and a reliable one. When installed by an Excel network accredited partner, you get the peace of mind of a 25 year equipment warranty. Understanding these basics helps you sidestep the common pitfalls and get your network performing properly.
Your WiFi Extender Questions Answered
Now that we’ve covered how WiFi extenders work, you probably have a few practical questions bubbling up. Let's tackle some of the most common ones that crop up when you're trying to get your home network just right.
Will My Extender Have a Different WiFi Network Name?
Yes, in most cases, it will. A standard WiFi extender creates a brand-new, separate network by repeating your main router's signal. You'll usually spot it in your WiFi list with the same name as your primary network, but with tacked onto the end.
This means you'll need to manually switch your phone, laptop, or tablet to the extender's network when you walk into an area with a weak signal. It's a fundamental part of how these devices fill in those frustrating dead zones.
Can I Use More Than One Extender in My House?
Technically, you can, but it's rarely a good idea. Adding multiple extenders often creates more problems than it solves. You can end up with signal interference and a sluggish, unreliable connection as each extender adds another "hop" for your data to make.
If you’re dealing with dead zones all over a large property, a mesh WiFi system is a much better solution. It uses multiple nodes to create a single, seamless network—a far more robust and efficient setup than daisy-chaining extenders.
Does a WiFi Extender Always Reduce My Internet Speed?
Unfortunately, yes. A speed reduction is just part of how the technology works. Most extenders operate in what’s known as 'half-duplex' mode, meaning they can't send and receive data at the same time on the same frequency band. This limitation effectively halves the available bandwidth for any device connected through the extender.
But remember the goal here: it's not about maintaining top speed. It's about getting a stable, usable connection in a room where you previously had nothing. A slightly slower but stable connection is always better than no connection at all.
For a professionally planned network that guarantees performance, from structured fibre cable installation to a fully optimised wireless setup, trust the experts. As an Excel network accredited partner, Constructive-IT delivers certified, tested network delivery with a 25 year equipment warranty. Learn more at https://www.constructive-it.co.uk.






Comments